Software Version Control is an important part of every modern software development team. Provided below are some of the best practices for working with software version control systems.
1. Commit Atomically
A separate commit should be done for every bug fix, feature addition or any meaningful modification in source code. However, it does not mean that every code change should produce a commit, because it would make a mess of version control system. As an example, fixing two different bugs should result in two separate commits. Small commits make it convenient for other developers to understand the changes and helps in debugging if some functionality is broken.
2. Commit Often
Committing often helps to keep a nice history and keep the commits small. This will make it convenient to integrate changes between multiple developers and avoid having merge conflicts.
3. Discuss Before Resolving Merge Conflicts
When resolving merge conflicts, it is a good practice to discuss it with other developers who committed the code as well.
4. Write Good Commit Messages
Write descriptive and meaningful commit messages to clearly identify the purpose of commit. A good commit message includes a short summary, followed by an explanation of the fix or feature added. You can also specify the type of commit like its a fix, feature or refactor. Do not copy-paste the actual code change (diff will tell that) or the issue tracker information in a commit message. Include a link to the feature or issue tracker id to maintain traceability. A good commit message is useful for code review and long term maintainability. A good commit message also helps in resolving merge conflicts and reverting changes later.
5. Commit Complete Work
You should only commit when you have completed the implementation. This does not mean that you forget to commit early and often. Do not commit with the sole purpose of keeping a backup of your code. Doing commits of complete work ensures that the code remains usable by other developers and does not break once other developers fetch fresh updates from remote repository.
6. Learn to Use Version Control
Version Control is the part and parcel of developer's every day job. You should master all the features and useful commands of specific Version Control System (VCS) you are using. Only then you would be able to utilize it efficiently to the full capability. Keep a cheat sheet of frequently used commands with you for quick reference.
7. Test Before You Commit
Do not commit unless you have tested your code locally on your machine, even if you think it's completed. Testing you code before pushing your changes to remote repository is very important since your code may be fetched by other developers in the team.
8. Version Control is not a Dedicated Backup System
Version Control is not a dedicated backup tool. Commit your changes once a feature or fix is completed, not after every few minutes only to backup your files. Although, Version Control tool keeps a backup and it can be used to revert to previous versions.
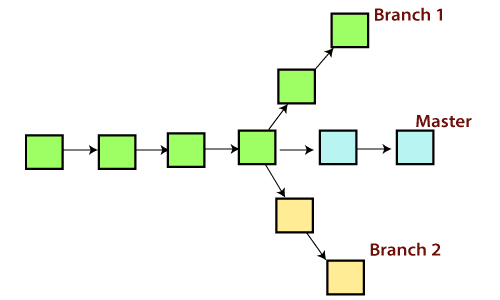
9. Use Branches
Use branches during your development for new features, bug fixes and refactoring. When you want to implement a new feature or a bug fix, you should spawn a new branch so that the master branch remains clean and protected.
10. Use Meaningful Branch Names
Use descriptive and meaningful names for the branches, based on a pre-defined template. Following good naming practices improves readability and helps to sort or identify branches at some later stage.
11. Follow the Agreed Workflow
Finalize and agree on a particular workflow or branching model with your team members and make sure that everyone follows the same workflow.
12. Do not Alter History
If you find out that you broke some functionality after you have pushed your changes to a remote repository, make a new commit and fix the problem instead of rewriting public history.
13. Use Tools
Use some good tools to help you work easily in a productive manner. Some of the popular tools for various platforms include GitHub, GitLab, Azure DevOps, Tower, QGit, Tortoise Git and SmartGit etc. For efficient and smooth working, integrate VCS with external tools related to issue tracking, chat rooms, DevOps and Wikis.
14. Do not Commit Configuration and Binary Files
Do not commit configuration files which might change from environment to environment. Similarly, do not commit large binary or executable files.
Provided above are some of the best practices for working with software Version Control Systems. Adopting these practices can help teams to improve their productivity regardless of their size and expertise.







Comments
Post a Comment